Our Technology
HZI Steinmüller delivers proven and market leading chute to stack Waste to Energy technologies capable of meeting and exceeding the strictest environmental standards with single line capacity up to 400,000 tons per annum.
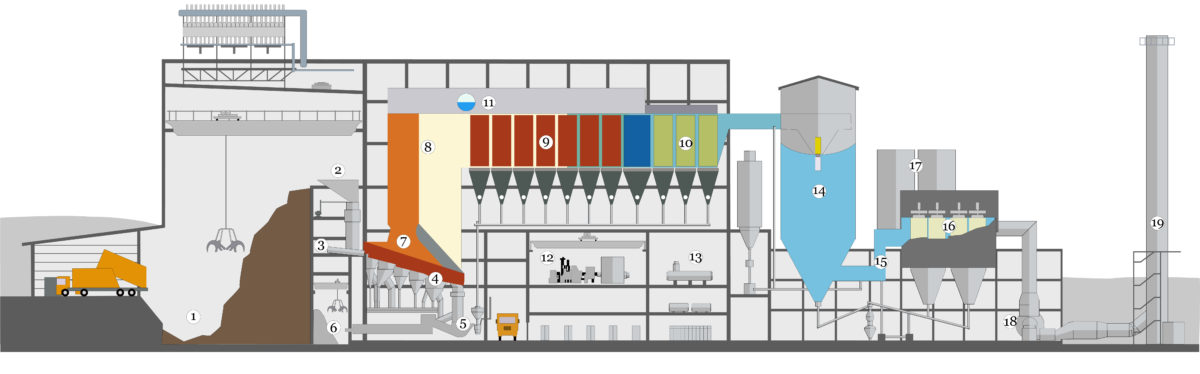
 Waste bunker: The waste delivered is stored in the waste bunker (1) and homogenised by the crane. The crane then transports the mixed waste to the feeding hopper (2). Via the chute the waste arrives at the feeder (3) which pushes the waste onto the combustion grate in accordance with the firing control requirements.
Waste bunker: The waste delivered is stored in the waste bunker (1) and homogenised by the crane. The crane then transports the mixed waste to the feeding hopper (2). Via the chute the waste arrives at the feeder (3) which pushes the waste onto the combustion grate in accordance with the firing control requirements.
 Grate: The Waste to Energy process takes place on the grate (4) which comprises of grate bar rows with grate bars side by side. The grate bar rows are arranged overlapping one behind the other. Every second row moves alternately forth and back.
Grate: The Waste to Energy process takes place on the grate (4) which comprises of grate bar rows with grate bars side by side. The grate bar rows are arranged overlapping one behind the other. Every second row moves alternately forth and back.
The waste and later the slag material is transported by these rows to the end of the grate where the slag is discharged into the slag extractor (5) .
 dry.xtract: The slag is being cooled down and transported to the slag bunker. Either a wet slag extractor or our dry.xtract system can by used.
dry.xtract: The slag is being cooled down and transported to the slag bunker. Either a wet slag extractor or our dry.xtract system can by used.
 Fire on grate: The combustion of residues is controlled by our active.ignite control system. Primary combustion air is fed from below into the steinmüller.grate. Secondary air is supplied above the steinmüller.grate to meet a specified oxygen content in the flue gas. To ensure safe burnout and total destruction of hazardous SUBSTANCES OUR SECONDARY AIR generates the patented Steinmüller double-vortex in the first duct to thoroughly mix the flues.
Fire on grate: The combustion of residues is controlled by our active.ignite control system. Primary combustion air is fed from below into the steinmüller.grate. Secondary air is supplied above the steinmüller.grate to meet a specified oxygen content in the flue gas. To ensure safe burnout and total destruction of hazardous SUBSTANCES OUR SECONDARY AIR generates the patented Steinmüller double-vortex in the first duct to thoroughly mix the flues.
 steinmüller.boiler: Feedwater from the feedwater tank (13) enters the Economizer (10) and is heated up close to boiling temperature. The water enters the steam drum (11) and is fed to the evaporator (8) to be transformed into steam. The so produced steam enters the superheater (9) and is subsequently fed to the steam turbine (12).
steinmüller.boiler: Feedwater from the feedwater tank (13) enters the Economizer (10) and is heated up close to boiling temperature. The water enters the steam drum (11) and is fed to the evaporator (8) to be transformed into steam. The so produced steam enters the superheater (9) and is subsequently fed to the steam turbine (12).
 Air quality control system: Lime stone based aborbents and water are used to remove pollutants from the flue gas in the Spray absorber (14). The pollutants react with the absorbents and form solid particles to be removed in the fabric filter (16). Reactants removed by the fabric filter are partly reused and injected together with additional raw absorbents in the entrained flow reactor (15). The remaining residues including fly ash from the combustion process are finally stored in the residue silos (17).
Air quality control system: Lime stone based aborbents and water are used to remove pollutants from the flue gas in the Spray absorber (14). The pollutants react with the absorbents and form solid particles to be removed in the fabric filter (16). Reactants removed by the fabric filter are partly reused and injected together with additional raw absorbents in the entrained flow reactor (15). The remaining residues including fly ash from the combustion process are finally stored in the residue silos (17).
 ID-fan: The ID-fan maintains underpressure in the firing system (7, 8) and feeds the flue gas from boiler (8-10) through the Air quality control system (14-17) into the stack (19).
ID-fan: The ID-fan maintains underpressure in the firing system (7, 8) and feeds the flue gas from boiler (8-10) through the Air quality control system (14-17) into the stack (19).
 Stack: Clean, pure water vapour is emitted from the stack in the form of white clouds which dissolve – a sign of optimum energy utilisation. The cleaned flue gas is leaving the process to atmosphere via the stack (19). In order to further improve efficiency, more and more condensation heat exchangers are installed in Waste to Energy plants.
Stack: Clean, pure water vapour is emitted from the stack in the form of white clouds which dissolve – a sign of optimum energy utilisation. The cleaned flue gas is leaving the process to atmosphere via the stack (19). In order to further improve efficiency, more and more condensation heat exchangers are installed in Waste to Energy plants.
WE DEVELOP DESIGN SUPPORT BUILD A CLEANER FUTURE
FULL OF ENERGY
STEINMÜLLER BOILER
The unique steinmüller.boiler is the key player in the energy recovery process: our boiler systems are efficiently producing steam under various conditions regarding corrosion, slagging, stress, part load conditions and overall system dynamics.
ALWAYS ON FIRE
GRATE
The performance and robustness of a Waste to Energy plant heavily relies on the combustion grate, often referred to as the heart of the plant. Our grate has demonstrated its robustness and reliability for many years in many reference plants and offers excellent fuel flexibility for all types of waste and is available in both air- and water cooled configurations.
OUT OF THE ASHES
DRY X TRACT
Waste to Energy highlights the abundance of resources available for extraction. The treatment not only recovers thermal energy, but also leaves behind residual substances, such as ash and slag. These solid materials form around 25% of the raw waste, however, a large proportion can be recycled with the help of our Dry X Tract System.
FIRE CONTROL
ACTIVE IGNITE
To improve efficiency in the plant, the HZI Steinmüller active.ignite System was developed for monitoring and adaptive optimisation of combustion. Our system automatically adapts to changing waste flow, waste composition and steam demand.



